Gadolinium
Gadolinium is a chemical element symbolized by Gd, belonging to the group of rare earth elements within the lanthanide series on the periodic table. It is characterized by its silvery-white appearance, and it exhibits both malleable and ductile properties, making it workable in various forms. Gadolinium stands out for its unique metallurgical characteristics, such as its ability to enhance the workability, resistance to oxidation, and ability to withstand high temperatures when alloyed with other metals like iron and chromium.
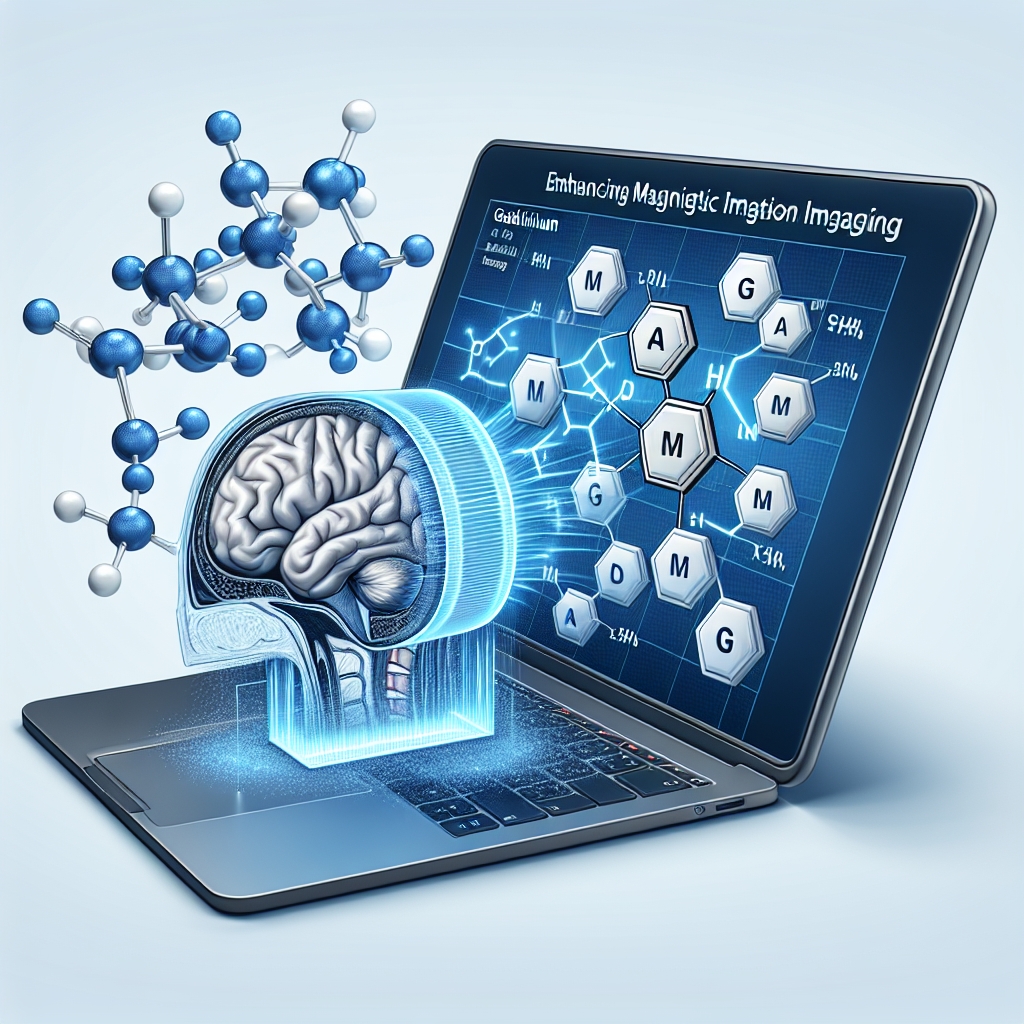
One of the most notable features of gadolinium is its magnetic properties. It is highly magnetic at temperatures below a certain point, which makes it valuable for use in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as a contrast agent. This application helps in improving the visibility of internal structures in the body during MRI scans.
Gadolinium also has a significant capacity to absorb neutrons, making it useful in nuclear reactors as a material to capture excess neutrons and help control nuclear reactions.
In the field of medicine, gadolinium compounds are utilized as contrast agents for MRI scans to enhance the clarity of the images obtained. This property is due to gadolinium’s ability to affect the relaxation times of atoms within the body, thereby improving the contrast of the MRI images.
Additionally, gadolinium finds applications in the manufacturing of electronic components and in the creation of alloys. It is used in making gadolinium yttrium garnets, which have applications in microwaves, and as a doping agent in materials designed to have specific optical properties.
Despite its various uses, gadolinium does not occur freely in nature. It is extracted from minerals such as monazite and bastnäsite, which contain small quantities of all the rare earth metals. Although gadolinium is more abundant than some other elements in the lanthanide series, it is still considered rare due to its sparse distribution in the Earth’s crust and the complex extraction processes required to isolate it.